57. The Agents
The Answer to Every Problem (Except the Ones They Create)
Welcome back to me. I took a month off to relax, recover, and give your inbox a little less of a strain. Let’s get back to it.
Stay for the commercial at the end of the clip!
Introduction
AI agents are a rapidly evolving technology poised to transform how humans interact with computers and software. These agents are not simply chatbots or single-purpose tools, but rather, they are intended to be autonomous entities that can perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals. They represent a shift from traditional software applications to more dynamic and personalized forms of computing.
What is an AI Agent?
At its core, an AI agent is a type of software that responds to natural language and can perform various tasks based on its understanding of the user. Unlike bots that are confined to a single application and require explicit instructions, agents are proactive, capable of learning user preferences and patterns, and can make suggestions before being asked ... They can operate across multiple applications and improve over time through their ability to remember past activities and recognize intent.
My Favorite Example
My favorite example - You want to take a vacation. Hotel, airfare, event tickets, tours. In theory your agent will …
Book the best deal on your airline of choice, complete with aisle seat.
You’re on the upgrade stand-by list (BTW).
Book the best deal with your hotel(s) of choice depending on number of destinations, of course.
Rental car, show tickets, and tours are all negotiated.
You are left with an itinerary with all planning completed.
You might ask, “Who is my agent interacting and negotiating with?” With all of the vendor agents, of course. Welcome to your new audience you‘ll be advertising to and currying favor with - bits of computer programming.
Key characteristics of AI agents include:
Autonomy: Agents can operate independently, making decisions and taking actions without constant human intervention ...
Personalization: Agents learn user preferences, behaviors, and needs, allowing for highly tailored experiences ...
Proactivity: Agents can anticipate user needs and take action without being explicitly prompted.
Task Completion: Agents can perform complex tasks that span multiple applications and services.
Learning: Agents can improve their performance and effectiveness over time by learning from user interactions and patterns.
And great news. You can begin today!
What is the Computer-Using Agent (CUA)?
From OpenAI Jan. 23, 2025
Today we introduced a research preview of Operator (opens in a new window), an agent that can go to the web to perform tasks for you. Powering Operator is Computer-Using Agent (CUA), a model that combines GPT-4o's vision capabilities with advanced reasoning through reinforcement learning. CUA is trained to interact with graphical user interfaces (GUIs)—the buttons, menus, and text fields people see on a screen—just as humans do. This gives it the flexibility to perform digital tasks without using OS- or web-specific APIs.
What is the Computer-Using Agent (CUA)?
Alright, so the CUA (Agent) is this fancy AI model that combines visual smarts from GPT-4's capabilities with advanced reasoning skills powered by reinforcement learning. What does that mean? It means the CUA (Agent) can look at graphical user interfaces (like buttons, menus, and text fields on your screen) and interact with them, just like a human would.
Here’s the kicker: CUA doesn’t rely on specific operating system or website APIs. Instead, it works by processing what it "sees" (raw pixel data, to be exact) and uses a virtual mouse and keyboard to get stuff done. Imagine having an assistant that can literally "see" your computer screen and take action based on what it sees. Cool, right?
How It Works
CUA operates in a loop of three steps:
Perception: It grabs screenshots from your computer and adds them to its memory.
Reasoning: Using chain-of-thought logic, it decides what to do next, analyzing screenshots and its past actions. Think of this as its inner monologue (scaaaaary).
Action: It performs tasks like clicking, typing, or scrolling until the job is done or it needs your input (like for sensitive stuff, such as login details).
What makes this AI even more impressive is its ability to adapt. If it runs into a hiccup, it can self-correct and figure out the next best step. In benchmarks, it’s already shown promising results, like achieving a 38.1% success rate on OSWorld tasks (which cover full computer use) and 87% success on web-based tasks in WebVoyager.
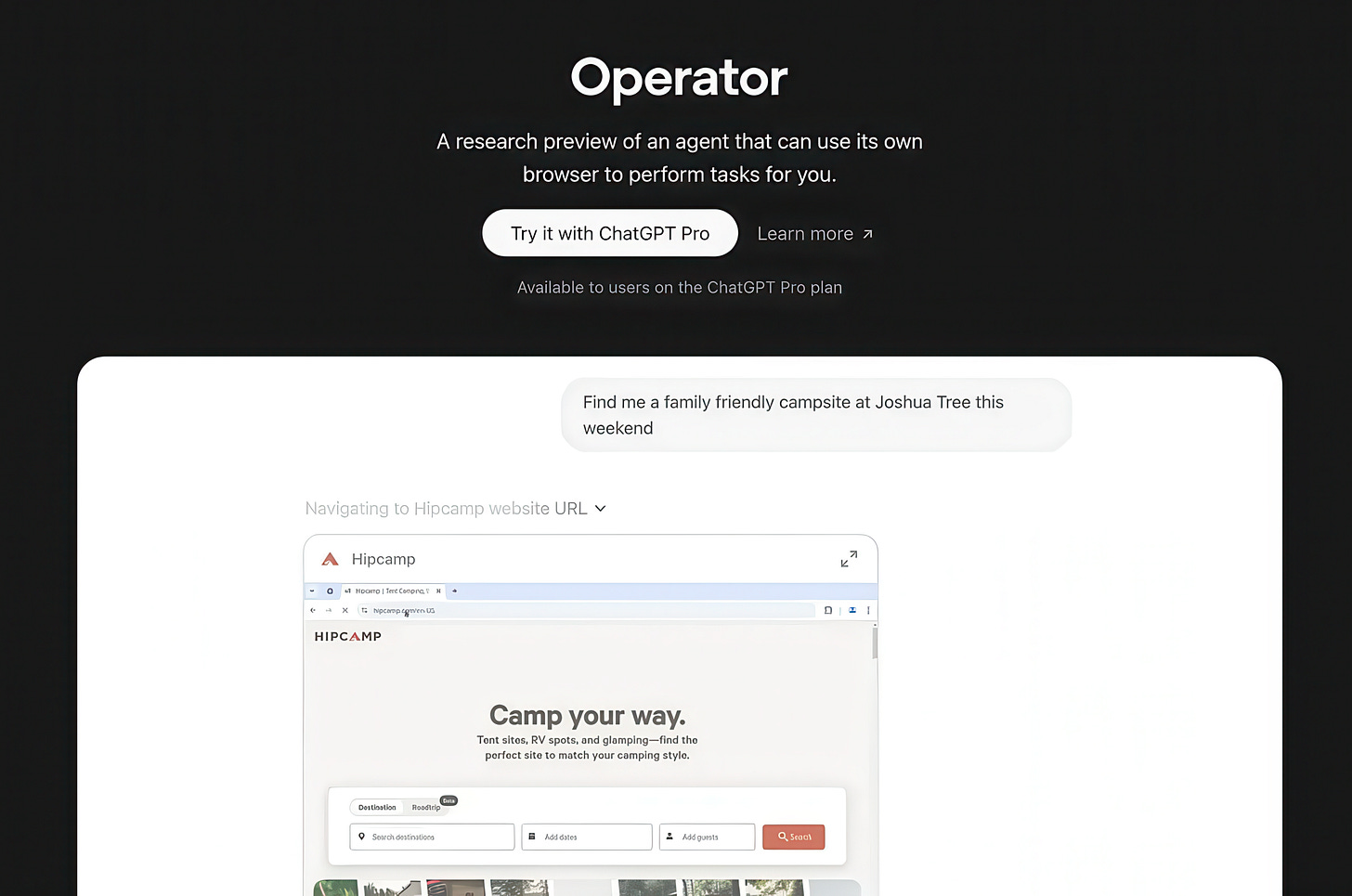
Meet Operator
CUA is part of an Open AI research preview called Operator, a web-based agent available to Pro users in the U.S. Operator lets you test out this technology in real-world scenarios, and your feedback helps improve its safety and performance.
It’s like being part of a sci-fi experiment—but in real life.
What can Operator do? Well, here are a few examples:
Interact with UI elements to search and filter results.
Automate repetitive tasks that might take you ages.
Create playlists on Spotify (yes, really)!
However, just like the rest of AI, it’s not perfect.
Operator might struggle with more complex or unfamiliar interfaces and tasks that require detailed instructions. But hey, it’s learning.
The Future of AI Agents in 2025
Fast forward to 2025, and AI agents like CUA are expected to be everywhere. They’ll be more proactive, personalized, and capable of doing even more on your behalf. Let’s break it down:
Increased Adoption: Businesses will jump on the AI bandwagon, integrating these agents into their operations.
Personalization: Imagine an AI that knows your preferences and acts like a true executive assistant. It’ll be able to handle tasks with minimal input from you.
Taking Action: AI agents won’t just give you answers; they’ll book your flights, manage your calendar, and more. Take your anxiety meds prior to handing over your credit card.
Autonomous Economies: These agents could even handle transactions, payments, and financial decisions. Think of them as "digital workers."
Better Multimodal Abilities: With enhanced interfaces, these agents will interact with both visual and browser-based platforms seamlessly.
Challenges and Considerations
Of course, with great power comes great responsibility. Here are a few challenges to think about:
Security: Keeping AI agents safe from misuse or hacking is a big concern.
Privacy: Who owns the data these agents use, and how is it stored?
Trust: Would you let an AI make important decisions for you?
Ethics: Ensuring these agents act in ways that align with human values is crucial.
Tech Hurdles: Implementing these systems isn’t easy. There’s a lot of work to be done on databases, interfaces, and more.
The Big Finish - The Tip of the Iceberg
OpenAI’s CUA and its role in tools like Operator are just the tip of the iceberg for what’s possible with AI agents. The future looks promising, but it’s essential to address the challenges to make sure this technology benefits everyone. Who knows? In a few years, you might have an AI agent that not only understands you but also takes care of your day-to-day tasks just as smoothly as your programmable Mr. Coffee. Is that even still a thing?
What do you think? Ready to let AI handle your to-do list? Baby steps.
If you find this edition of value please feel free to leave a note in the comments. And if you’re so inclined, you can now even buy me a cup of coffee.☕️☕️☕️☕️☕️
Please help share this far and wide:
Like this post!
Re-stack it below!
Share this post on Substack and other social media sites:
Feedback is always helpful.
Thanks for the read!
-pb
BTW - in case you haven’t seen this in a while …